Introduction to Osteodystrophy
Osteodystrophy is a common medical condition that affects the bones. This disorder occurs due to an imbalance in the bone mineral metabolism, leading to weakened and deformed bones. As a blogger who has extensively researched this topic, I am here to help you understand osteodystrophy, its causes, symptoms, and treatment options. The information provided in this article can be beneficial for those who are suffering from this condition or have a loved one who is affected by it. So, let's dive into the world of osteodystrophy and learn more about this complex bone disorder.
Causes of Osteodystrophy
There are several causes of osteodystrophy, with the most common being chronic kidney disease. When the kidneys fail to function properly, they are unable to excrete excess phosphorus, which leads to a buildup of phosphorus in the blood. This high level of phosphorus is harmful to the bones and can cause osteodystrophy.
Another cause of osteodystrophy is a deficiency of vitamin D. Vitamin D is essential for the proper absorption of calcium, which is necessary for maintaining strong and healthy bones. When there is a lack of vitamin D in the body, calcium levels decrease, and the bones become weak and brittle. This can eventually lead to osteodystrophy.
In addition to kidney disease and vitamin D deficiency, other factors that can contribute to the development of osteodystrophy include hormonal imbalances, hereditary factors, and certain medications. Understanding the underlying cause of osteodystrophy is essential for determining the appropriate course of treatment.
Recognizing the Symptoms of Osteodystrophy
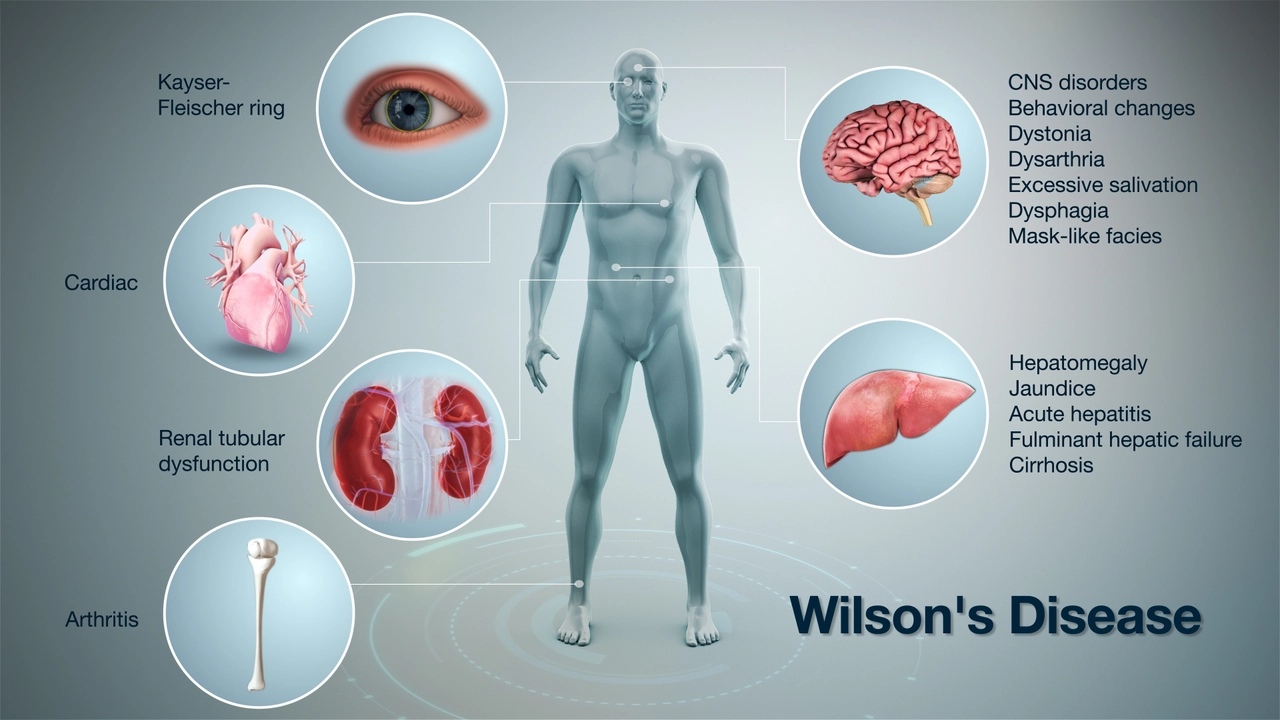
Osteodystrophy can manifest in several ways, with some of the most common symptoms being bone pain, muscle weakness, and deformities. Bone pain is often described as a deep, aching sensation that can affect any part of the body. Muscle weakness can make it difficult to perform everyday tasks, such as walking, lifting objects, or even sitting up straight.
Deformities in the bones are another telltale sign of osteodystrophy. These deformities can include bowing of the legs, an abnormal curvature of the spine, or a protruding chest. In severe cases, these deformities can be quite debilitating and may require surgical intervention to correct.
Other symptoms of osteodystrophy can include fractures, joint pain, and a decrease in height. If you or someone you know is experiencing these symptoms, it is crucial to consult with a healthcare professional for a proper diagnosis and treatment plan.
Diagnosing Osteodystrophy
Diagnosing osteodystrophy involves a comprehensive evaluation, including a thorough medical history, physical examination, and various diagnostic tests. Blood tests are often used to assess levels of calcium, phosphorus, and vitamin D, as well as kidney function. These tests can help determine whether an imbalance in bone mineral metabolism is present.
Imaging studies, such as X-rays, CT scans, or MRI, can also be useful in diagnosing osteodystrophy. These imaging techniques can reveal abnormalities in the bones, such as fractures or deformities, that may not be apparent during a physical examination.
In some cases, a bone biopsy may be performed to obtain a sample of bone tissue for further analysis. This can provide valuable information about the structure and composition of the bone, which can help guide treatment decisions.
Treatment Options for Osteodystrophy
The treatment of osteodystrophy is typically focused on addressing the underlying cause of the disorder and managing the symptoms. For individuals with chronic kidney disease, treatment may involve dialysis or a kidney transplant to improve kidney function and reduce phosphorus levels in the blood.
Vitamin D supplementation is often prescribed to help increase calcium absorption and promote healthy bone mineralization. In some cases, medications called phosphate binders may be used to help reduce the absorption of phosphorus from the diet, thereby lowering blood phosphorus levels.
For those with hormone-related osteodystrophy, treatment may involve hormone replacement therapy to help regulate hormone levels and improve bone health. In cases where bone deformities are severe, surgical intervention may be necessary to correct the deformity and improve overall function and mobility.
Preventing Osteodystrophy
Preventing osteodystrophy involves maintaining a healthy lifestyle and addressing any underlying medical conditions that may contribute to the development of the disorder. Some preventative measures include maintaining a balanced diet rich in calcium and vitamin D, getting regular exercise, and avoiding smoking and excessive alcohol consumption.
For individuals with chronic kidney disease, working closely with healthcare professionals to manage the condition and maintain proper kidney function can help prevent the development of osteodystrophy. Regular check-ups and monitoring of blood levels of calcium, phosphorus, and vitamin D can also aid in early detection and treatment of the disorder.
Living with Osteodystrophy
Living with osteodystrophy can be challenging, but with the right treatment and support, individuals can lead a fulfilling life. It is essential to work closely with healthcare professionals to develop a comprehensive treatment plan that addresses the underlying cause of the disorder and manages the symptoms.
In addition to medical treatment, individuals with osteodystrophy may benefit from physical therapy, occupational therapy, and pain management strategies to help improve function, mobility, and overall quality of life. Support groups and counseling can also be beneficial in coping with the emotional challenges that often accompany living with a chronic medical condition.
Understanding the Emotional Impact of Osteodystrophy
It is essential to recognize that osteodystrophy can have a significant emotional impact on individuals and their loved ones. The physical symptoms and limitations associated with the disorder can lead to feelings of frustration, isolation, and depression.
Seeking support from friends, family members, and healthcare professionals can be instrumental in coping with these challenges. Participating in support groups or counseling sessions can provide a safe space to share experiences, ask questions, and receive encouragement from others who are going through similar situations.
The Importance of Patient Advocacy
As a person living with osteodystrophy or as a caregiver, it is crucial to be an advocate for your health or the health of your loved one. This involves staying informed about the latest advancements in osteodystrophy research and treatment options, communicating openly with healthcare professionals, and ensuring that your needs and concerns are being addressed.
By taking an active role in your healthcare or the care of your loved one, you can ensure that the best possible treatment plan is developed, and any necessary adjustments are made as needed. Remember, you are not alone in your journey with osteodystrophy, and there are many resources and support networks available to help you along the way.
Conclusion
Osteodystrophy is a complex bone disorder that can significantly impact an individual's quality of life. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for this condition can help you or your loved one better manage the disorder and lead a fulfilling life. Remember, it is essential to work closely with healthcare professionals and maintain open communication to ensure that the best possible treatment plan is in place. With the right support, individuals with osteodystrophy can overcome the challenges they face and thrive.





Honestly, this is one of the clearest breakdowns of osteodystrophy I've seen. I've got a cousin with CKD and this helps explain why her bones keep cracking like dry twigs. No jargon, just facts. Thanks.
Oh wow, another ‘educational’ post that somehow forgets to mention that Big Pharma sells the exact meds that keep this going. Vitamin D? Sure. But have you checked the cost of those phosphate binders? 😏
This article is... acceptable. But you missed the fact that osteodystrophy is almost exclusively a result of American dietary failures-high phosphorus additives in processed foods, vitamin D deficiency due to indoor lifestyles, and lazy healthcare systems. In countries with real nutrition, this doesn't happen.
bro i had no idea this was even a thing. my grandma had weird back pain for years and they just called it 'old age'. guess she had this whole time. rip.
I'm from India, and I've seen this in elderly patients with poor nutrition and limited sun exposure. It's heartbreaking because so many don't have access to blood tests or supplements. Simple vitamin D drops could prevent so much suffering if distributed properly.
Phosphate binders are wild. They’re basically chalk pills you swallow with meals. Feels like eating dirt to avoid bone rot.
This is all a lie. Osteodystrophy is caused by fluoride in the water. The CDC and WHO are covering it up. Look at the correlation between fluoridated cities and bone deformities. 🤫👁️
The diagnostic criteria outlined here are clinically sound. However, I would emphasize the importance of early intervention with calcitriol in patients with stage 3-4 CKD. Delayed treatment leads to irreversible skeletal changes.
You say vitamin D deficiency is a cause-but have you considered that most people in the West are deficient because they refuse to go outside? It’s not a medical problem, it’s a laziness problem. My grandmother in Kerala walked barefoot at dawn and never had a bone issue. Modern life is killing us.
You’re telling me this isn’t just a side effect of the government’s push for low-fat diets? No fat means no vitamin D absorption. This is systemic negligence. And now we’re paying for it with brittle bones.
my aunt got diagnosed last year and started taking D3 + calcium + walking 20 mins a day... her pain is gone. 💪🌿 just saying. small changes matter.
This is why we need to stop treating symptoms and start treating the soul. Osteodystrophy isn't just about minerals-it's about disconnection. We've lost touch with nature, with rhythm, with ancestral wisdom. The bones know. They're screaming for us to remember.
I've been living with this for 12 years. Doctors told me it was 'just aging.' I found out it was CKD from undiagnosed diabetes. I'm 43. I don't feel old. I feel betrayed. If you're reading this and have chronic pain-get your labs done. Don't wait.
I work in nephrology. This summary is accurate, but I’d add that dietary phosphorus is often hidden-processed cheese, colas, even some breads. Patients don’t realize they’re poisoning themselves with convenience food. Education is the real treatment.
The most effective prevention is routine screening for at-risk populations. No excuses. If you have diabetes, kidney disease, or are over 60-get your calcium, phosphorus, and PTH checked yearly. It's simple. It's cheap. It saves lives.