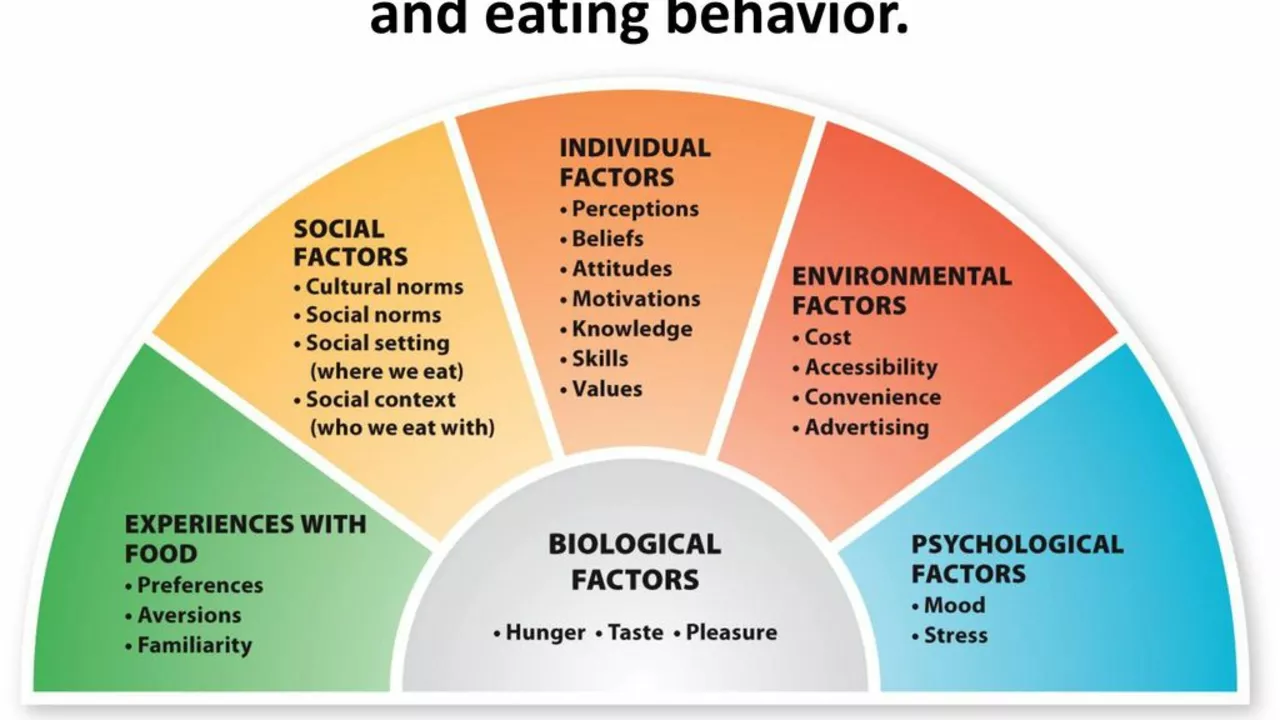
Understanding Obesity
Before diving into the socioeconomic factors that influence obesity, it's important to have a clear understanding of what obesity is. Obesity is a complex health condition characterized by excessive body fat. It is generally determined by calculating the Body Mass Index (BMI), but it's much more than just a number on a scale. This health condition is associated with a plethora of diseases including heart disease, type 2 diabetes, certain types of cancer, and even mental health issues like depression and anxiety.
The Socioeconomic Spectrum and Obesity
Socioeconomic status is a measure of a person's social standing, wealth, and access to resources. It's a composite of education, income, and occupation. Studies have shown that there is a clear link between socioeconomic status and obesity rates. People from lower socioeconomic backgrounds are more likely to be obese than those from higher socioeconomic backgrounds.
Food Accessibility and Affordability
Availability and affordability of healthy food options play a major role in the obesity epidemic. In many low-income neighborhoods, fresh, nutritious food is hard to come by. These areas, known as 'food deserts,' often have a proliferation of fast food outlets and convenience stores rather than supermarkets with fresh produce. The high cost of healthy foods compared to cheaper, calorie-dense junk foods further exacerbates this problem.
The Impact of Education
Education is a powerful tool in combating obesity. Levels of education influence dietary choices, understanding of nutrition labels, and the ability to make informed health decisions. People with lower education levels tend to have higher rates of obesity, likely due to lack of knowledge about healthy eating habits and the long-term consequences of an unhealthy diet.
Income Disparities and Obesity
Income is another major factor in obesity rates. Lower-income individuals often struggle to afford gym memberships, recreational sports, or even safe outdoor spaces for exercise. Additionally, high stress levels associated with financial instability can lead to emotional eating and unhealthy food choices.
The Role of Occupation
Occupation directly affects our levels of physical activity and, consequently, our weight. Sedentary jobs, common among the middle and upper classes, contribute to weight gain and obesity. On the other hand, physically demanding jobs, often held by lower-income individuals, can also lead to obesity due to irregular eating patterns and dependence on convenience foods.
Urbanization and Obesity
The fast-paced urban lifestyle often leads to unhealthy eating habits and sedentary behaviors, contributing to higher obesity rates. Limited access to green spaces, heavy reliance on cars instead of active transportation, and high-stress environments are all factors in the urban obesity equation.
Healthcare Access and Obesity
Access to healthcare plays a crucial role in the fight against obesity. Regular check-ups can help detect early weight gain and provide guidance on nutrition and exercise. Unfortunately, those with low incomes often lack access to quality healthcare, missing out on these preventive measures.
Stress and Obesity
Stress is a common thread that runs through many of these socioeconomic factors. Chronic stress, common among those with low socioeconomic status, can lead to overeating and unhealthy food choices, contributing to obesity.
Policy Interventions for Obesity
Understanding the socioeconomic factors influencing obesity rates is key in designing effective policies. Interventions like improving access to healthy foods in low-income neighborhoods, promoting physical activity, and providing education on healthy eating can help combat this public health crisis.





I've seen this firsthand in my hometown. My neighbor works two jobs just to keep food on the table, and the only thing that's affordable is frozen pizza and soda. It's not about willpower-it's about survival.
Why do we keep blaming people instead of fixing the system?
Honestly, it’s wild how we treat obesity like a moral failing when it’s really a structural failure. People aren’t lazy-they’re just trapped in systems designed to make healthy choices hard.
Also, have you ever tried buying kale in a food desert? It’s like searching for a unicorn.
Oh wow, so the poor are just too dumb to eat salad? How novel.
Meanwhile, the rich are out here paying $18 for avocado toast and calling it ‘self-care’ while their kids have personal trainers. The irony is thicker than a double bacon cheeseburger.
This is why America is falling apart!! We've allowed socialist policies to destroy personal responsibility!! If people just stopped eating junk food and started running, they wouldn't be fat!!
Also, the government is lying about BMI! It's a plot by Big Pharma to sell more pills!!
Let me tell you something, my dear, you are all missing the deeper truth. In India, where I come from, we used to eat rice with lentils and vegetables, and our grandmothers walked miles every day. Now, our youth are addicted to McDonald's and Netflix, and they wonder why they are overweight. It's not just food-it's cultural decay. The West has exported its poison, and now we are all paying the price. You cannot fix obesity without fixing the soul.
The data is clear: access to nutrition education and affordable physical activity opportunities significantly reduces obesity prevalence. Public health funding must prioritize these interventions over reactive medical treatments.
Food deserts are real. Also, gyms are expensive. Simple.
bro i used to work at a gas station in detroit and the only thing we had was cheetos and pop tarts. people would buy 3 bags of chips and a 2 liter of coke for $5. nobody’s lazy, we’re just broke. also, who has time to cook when you’re working 12 hour shifts?
You people are so naive. This isn’t about food-it’s about the global elite controlling the population through sugar and corn syrup. They want you fat, docile, and distracted. Wake up. The FDA is in on it.
I know what's really going on... They put fluoride in the water to make us sleepy so we eat more. And the schools? They serve processed meals because the government is working with the food giants. I've seen the documents. I'm not crazy. I'm just the only one who sees it. 😔👁️
We need policy change, not blame. Invest in community kitchens, subsidize produce, mandate nutrition in schools. That’s the solution.
I just feel like... we’re all just lost souls in a capitalist hellscape trying to find meaning in a bag of Doritos. I mean, when your life is falling apart, what’s left? A snack? A hug? A 3am TikTok scroll? I’m not judging. I’ve been there. 🥲
i get it. when you're exhausted and stressed and your kid needs dinner in 10 minutes, you grab what's quick. no one's choosing obesity. we're choosing survival. 🫂
You think this is about food? No. It’s about weakness. Weakness of character. Weakness of will. My grandfather worked in a factory for 40 years and never ate junk. He didn’t need a ‘food desert’-he had discipline. You people are weak. That’s why you’re fat.
The real issue isn't just access-it's dignity. When people are constantly told they're the problem, they stop trying. We need to build systems that honor people's realities, not shame them.
Let’s not forget the cultural layer: in many communities, food is love. A home-cooked meal isn’t just calories-it’s legacy. When you take away that tradition without replacing it with something equally meaningful, you’re not solving obesity-you’re erasing identity. We need culturally competent nutrition programs, not just kale pamphlets.
Your entire argument is based on pseudoscientific correlation. BMI is a flawed metric. Obesity is not a disease. It’s a natural variation. And your ‘food deserts’? They’re just markets with different inventory. Stop infantilizing people. They can walk to the store. They just choose not to.
You really think people in Flint, Michigan, are just lazily ignoring kale because they’re too weak to walk two blocks? That’s not just ignorant-it’s cruel.
There are entire zip codes where the nearest grocery store is 12 miles away, and public transit doesn’t run after 7pm. You don’t get to call someone’s survival choice ‘weakness’ when you’ve never been hungry.