Understanding Hiatal Hernia and its Symptoms
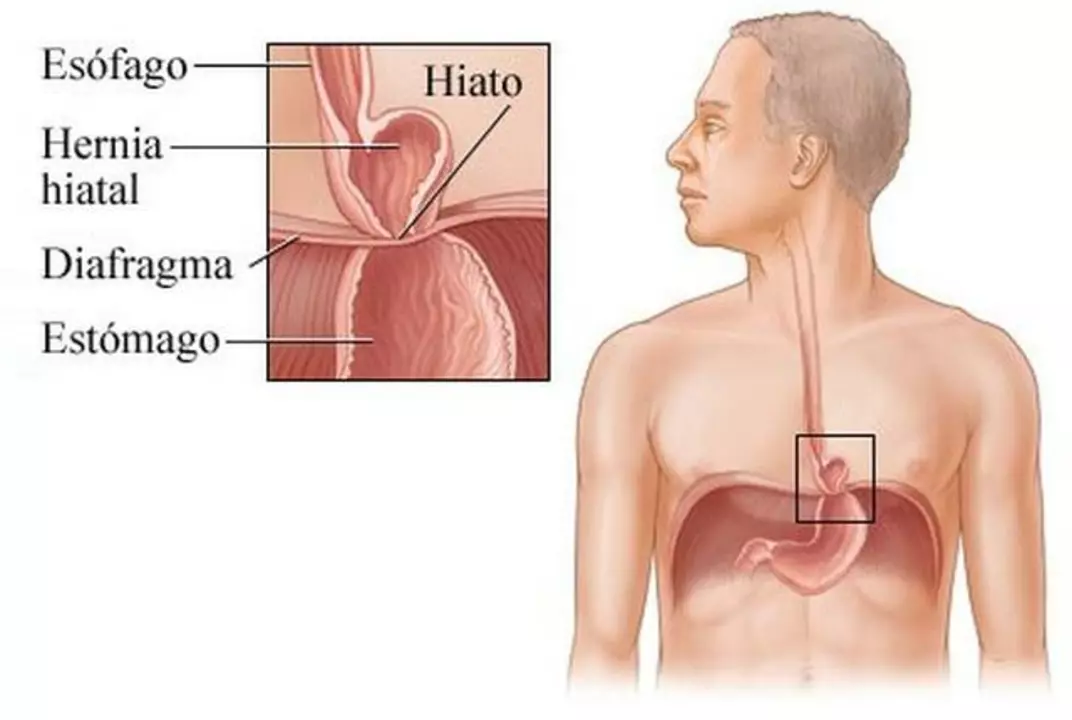
Before delving into the relationship between Ranitidine and hiatal hernia, it is essential to understand what a hiatal hernia is and its symptoms. A hiatal hernia occurs when the upper part of the stomach pushes through an opening in the diaphragm and moves into the chest cavity. This can cause various symptoms such as heartburn, chest pain, difficulty swallowing, and regurgitation of food or liquids. In some cases, a hiatal hernia might not cause any noticeable symptoms and can only be discovered during a routine medical examination.
The severity of symptoms can vary from person to person and is often influenced by factors such as the size of the hernia, the individual's overall health, and their lifestyle choices. Some common symptoms of a hiatal hernia include:
- Heartburn and acid reflux
- Difficulty swallowing
- Chest pain
- Regurgitation
- Shortness of breath
- Bloating and belching
- Nausea
What is Ranitidine and How Does it Work?
Ranitidine, also known as Zantac, is a medication that belongs to a class of drugs called histamine-2 (H2) blockers. These drugs work by reducing the amount of acid produced in the stomach. Ranitidine is commonly prescribed to treat conditions such as gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), peptic ulcers, and heartburn caused by acid reflux. By lowering the production of stomach acid, Ranitidine can help alleviate the symptoms associated with these conditions and promote healing of the damaged esophagus or stomach lining.
It is important to note that while Ranitidine can provide relief from the symptoms of a hiatal hernia, it does not address the underlying cause of the hernia itself. In some cases, additional treatment methods such as lifestyle changes, weight loss, or surgery may be necessary to manage a hiatal hernia effectively.
The Benefits of Ranitidine for Hiatal Hernia Sufferers
For individuals struggling with the symptoms of a hiatal hernia, the use of Ranitidine can offer several benefits. These include:
- Reduced heartburn and acid reflux: By decreasing stomach acid production, Ranitidine can help alleviate the burning sensation and discomfort associated with heartburn and acid reflux.
- Improved digestion: Lowering stomach acid levels can aid digestion, reducing feelings of bloating, gas, and nausea that may accompany a hiatal hernia.
- Faster healing of the esophagus: By controlling acid reflux, Ranitidine can promote the healing of the damaged esophagus, reducing the risk of complications such as esophagitis or Barrett's esophagus.
- Prevention of complications: Long-term use of Ranitidine can help prevent complications such as esophageal strictures or ulcers in individuals with chronic acid reflux caused by a hiatal hernia.
Ranitidine Dosage and Administration
It is important to follow your healthcare provider's instructions when taking Ranitidine for the treatment of hiatal hernia symptoms. The dosage and frequency of administration will vary depending on the severity of your symptoms, your overall health, and any other medications you may be taking. Generally, Ranitidine is taken once or twice daily, either with or without food. It is crucial to take this medication consistently and as prescribed to achieve the best results and prevent a relapse of symptoms.
If you are unsure about the proper dosage or administration of Ranitidine, consult with your healthcare provider for guidance. Also, inform them of any other medications or supplements you are taking to avoid potential drug interactions.
Potential Side Effects of Ranitidine
As with any medication, Ranitidine can cause side effects in some individuals. Common side effects of Ranitidine include:
- Headache
- Dizziness
- Constipation or diarrhea
- Nausea and vomiting
- Abdominal pain
Most side effects of Ranitidine are mild and can be managed with over-the-counter medications or by adjusting the dosage of Ranitidine. However, if you experience severe or persistent side effects, contact your healthcare provider for advice.
In rare cases, Ranitidine can cause more serious side effects, such as:
- Severe allergic reactions
- Difficulty breathing
- Irregular heartbeat
- Seizures
- Yellowing of the skin or eyes (jaundice)
If you experience any of these serious side effects, seek immediate medical attention.
When to Consider Alternative Treatments
While Ranitidine can be effective in providing relief from the symptoms of a hiatal hernia, it is not a suitable treatment option for everyone. If you are pregnant, breastfeeding, or have a history of liver or kidney problems, consult with your healthcare provider to determine if Ranitidine is the right choice for you. Additionally, if you have been taking Ranitidine for an extended period and your symptoms have not improved or worsened, it may be time to consider alternative treatments.
Several other medications and treatment options can help manage the symptoms of a hiatal hernia, including proton pump inhibitors (PPIs), antacids, and lifestyle modifications such as diet changes and weight loss. In some cases, surgical intervention may be necessary to correct the hernia and provide long-term relief from symptoms.
Conclusion
In conclusion, Ranitidine can provide relief from the symptoms of a hiatal hernia by reducing stomach acid production and alleviating heartburn, acid reflux, and other associated symptoms. However, it is essential to remember that Ranitidine does not address the underlying cause of a hiatal hernia and may not be suitable for everyone. Always consult with your healthcare provider to determine the best course of treatment for your specific situation, and keep them informed of any changes in your symptoms or overall health.






Ranitidine helped me big time with my acid reflux, but I didn't even know I had a hiatal hernia until my doctor mentioned it during an endoscopy. Funny how your body just whispers until it screams.
Whoa-wait, ranitidine got pulled?? Why are we even talking about this?? The FDA banned it for a reason!! This post is outdated and dangerous!!
lol i took zantac for years and never thought twice. then one day my pharmacist just says 'hey you shouldn't be taking this anymore' and i'm like... oh. guess i'm switching to pepcid. no biggie.
I'm not a doctor, but I’ve been living with a sliding hiatal hernia for 12 years. Ranitidine? It worked like a charm for years. But after the recall, I switched to omeprazole and honestly? It’s been worse. The heartburn came back harder. I’m now on famotidine-same class, different drug. Don’t panic, just adapt.
For anyone reading this: if you're on ranitidine, talk to your doc. Don't just quit cold turkey. Your stomach acid will go nuts. I went from 0 heartburn to 'why is my chest on fire?' in 48 hours. Gradual switch, low acid diet, and sleep propped up saved me.
So let me get this straight-you're recommending a banned drug because it 'worked'? That's like saying 'I used to smoke menthols and felt fine' so everyone should start again. You're not helping, you're endangering people. This is why medicine is broken.
Hiatal hernia + GERD is a lifestyle game, not a pill game. I lost 45 lbs, stopped eating after 7pm, and slept on a wedge. No meds needed. Ranitidine? Sure, it masked it. But real relief? That’s in your fork and your pillow.
just switched to famotidine last month 😌 no more burning 😭 also started sleeping on my left side and it’s like a whole new life. also… i know this isn’t medical advice but i love u all 💖
Of course the article doesn’t mention NDMA contamination. Because why ruin a nice little comfort story with facts? Ranitidine was a ticking time bomb disguised as a pill. Thank you, FDA, for finally doing your job.
Bro, I’ve had this hernia since I was 19. I used to pop ranitidine like candy. Now I drink ginger tea, chew gum after meals, and wear compression shirts. No drugs. No surgery. Just discipline. You can do it too. The body heals when you stop feeding it poison.
Why are we still talking about this? This drug was pulled because it was carcinogenic. Americans think 'it worked for me' is a valid medical argument. We're not in a Netflix documentary. This isn't a personal testimonial thread. It's public health.
Did you know the FDA didn't pull ranitidine because of safety? It was because the manufacturers knew about the NDMA levels for years and covered it up. This is Big Pharma gaslighting. They want you to think it's 'just a recall'-but it's a cover-up. Wake up.
Always consult your physician before changing medications. Ranitidine may have been effective for symptom management, but it did not treat the anatomical cause of hiatal hernia. Current guidelines recommend PPIs or H2 blockers without NDMA risk, such as famotidine, alongside behavioral modifications.
They took Zantac away and now we're all just... suffering. Like, what even is life anymore? I used to sleep through the night. Now I'm up at 3am with a burning throat, wondering if the government hates me. I miss my little blue pill. I miss my peace.
The entire premise of this article is flawed. Ranitidine was never intended to treat hiatal hernia-it was designed for GERD. A hiatal hernia is a mechanical defect. You cannot pharmacologically correct a structural anomaly. This is medical reductionism at its finest. The author misunderstands physiology.
Let me tell you something, because I’ve been researching this for months and I’ve read every study, every meta-analysis, every FDA advisory, and I’ve spoken to three gastroenterologists and one pharmacist who used to work at GlaxoSmithKline-ranitidine was a time bomb, and anyone who says otherwise is either naive, misinformed, or worse, financially incentivized. The fact that this article even exists without a bold, flashing warning is irresponsible. You don’t just swap one pill for another-you restructure your entire life. And if you think this is just about heartburn, you’re missing the forest for the trees. Acid reflux is a symptom, not the disease. The disease is your lifestyle. Your diet. Your stress. Your sleep. Your posture. Your emotional state. And if you’re still relying on pills to fix what your choices broke, you’re not healing-you’re delaying the inevitable.
Did you know ranitidine was linked to a secret CIA program in the 90s? They were testing it as a mind-control agent. That’s why it was pulled-not because of NDMA, but because people started reporting ‘spontaneous philosophical insights’ and ‘unwanted empathy.’ The government didn’t want you feeling too connected to your body. They want you medicated, quiet, and obedient. I’ve been off it for 7 years. My soul is finally free.
Wait-so you're recommending a drug that was recalled due to carcinogenic impurities? And you're not even mentioning the 2020 class-action lawsuit? Or the fact that 87% of patients who switched to famotidine reported better outcomes? This article is dangerously incomplete. Someone needs to fact-check this before it kills someone.
People don’t understand-this isn’t about pills. It’s about surrender. I spent 10 years fighting my body with antacids. Then I stopped. I stopped fighting. I started listening. I ate slower. I stopped lying down after meals. I cried more. And guess what? The hernia didn’t vanish-but the pain did. Sometimes healing isn’t about fixing-it’s about accepting.
Based on the current literature and the 2020 FDA recall, the continued endorsement of ranitidine as a therapeutic agent for hiatal hernia-related symptoms constitutes a clear violation of evidence-based medical guidelines. The presence of N-nitrosodimethylamine (NDMA), a probable human carcinogen, in multiple lots of ranitidine formulations, coupled with documented dose-dependent accumulation in human plasma, renders its use ethically and clinically indefensible. Furthermore, the substitution of ranitidine with famotidine or proton pump inhibitors is not merely a pharmacological adjustment-it is a mandatory clinical imperative. Any healthcare provider who continues to prescribe ranitidine post-recall is potentially liable for negligence. Please, for the love of all that is medical, stop normalizing this.